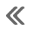Suzuki GSX-R 1000 Service Manual: Injection timing description
Injection time (injection volume)
The factors to determine the injection time include the basic fuel injection time, which is calculated on the basis of the intake air pressure, engine speed and throttle opening angle, and various compensations. These compensations are determined according to the signals from various sensors that detect the engine and driving conditions.
Compensation of injection time (volume)
The following different signals are output from the respective sensors for compensation of the fuel injection time (volume).
|
Signal |
Descriptions |
| Atmospheric pressure sensor signal | When atmospheric pressure is low, the sensor sends the signal to the ecm and reduce the injection time (volume). |
| Engine coolant temperature sensor signal | When engine coolant temperature is low, injection time (volume) is increased. |
| Intake air temperature sensor signal | When intake air temperature is low, injection time (volume) is increased. |
| Heated oxygen sensor signal | Air/fuel ratio is compensated to the theoretical ratio from density of oxygen in exhaust gas. The compensation occurs in such a way that more fuel is supplied if detected air/fuel ratio is lean and less fuel is supplied if it is rich. |
| Battery voltage signal | Ecm operates on the battery voltage and at the same time, it monitors the voltage signal for compensation of the fuel injection time (volume). A longer injection time is needed to adjust injection volume in the case of low voltage. |
| Engine rpm signal | At high speed, the injection time (volume) is increased. This is the compensation of the srad. |
| Starting signal | When starting engine, additional fuel is injected during cranking engine. |
| Acceleration signal/deceleration signal | During acceleration, the fuel injection time (volume) is increased,
in accordance with the throttle opening speed and engine rpm. During deceleration, the fuel injection time (volume) is decreased. |
Injection stop control
|
Signal |
Descriptions |
|
| Tip-over sensor signal (fuel shut-off) | When the motorcycle tips over, the tip-over sensor sends a signal to the ecm. Then, this signal cuts off current supplied to the fuel pump, fuel injectors and ignition coils. | |
| Over-rev. Limiter signal | The fuel injectors stop operation when engine rpm reaches rev. Limit rpm. The fuel cut-off circuit is incorporated in this ecm in order to prevent over-running of engine. When engine speed reaches 13 500 r/min, this circuit cuts off fuel at the fuel injectors. But under no load, the clutch lever is pulled or the gear position is in neutral, this circuit cuts off fuel when engine speed reaches 13 100 r/min.
|
 Self-diagnosis function
Self-diagnosis function
The self-diagnosis function is incorporated in the ecm. The function has two
modes, “user mode” and “dealer mode”.
The user can only be notified by the lcd (display) panel and led (fi indicator
...
Other materials:
Headlight
To replace the headlight bulbs,
perform the following steps:
Upper light bulb
Remove the bolt 1 to lift the
instrument panel 2.
Turn the cap 3 counterclockwise
and remove it.
Unhook the bulb holder spring
4 and pull out the socket 5.
Pull off the bulb from ...
Specifications
Service data
Wheel
unit: mm (in)
Tire
Tightening torque specifications
Note
the specified tightening torque is described in the following.
“Front wheel components” “front wheel assembly construction”
“rear wheel components” “rear wheel assembly c ...
Rear shock absorber adjustment
After installing the rear suspension, adjust the spring
pre-load and damping force as follows:
Spring pre-load adjustment
The set length 179.3 Mm (7.06 In) provides the
maximum spring pre-load.
The set length 189.3 Mm (7.45 In) provides the
minimum spring pre-load.
Std position
184.3 ...

 Caution
Caution